Septoplasty
What is Septoplasty?
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure to correct a deviated nasal septum.
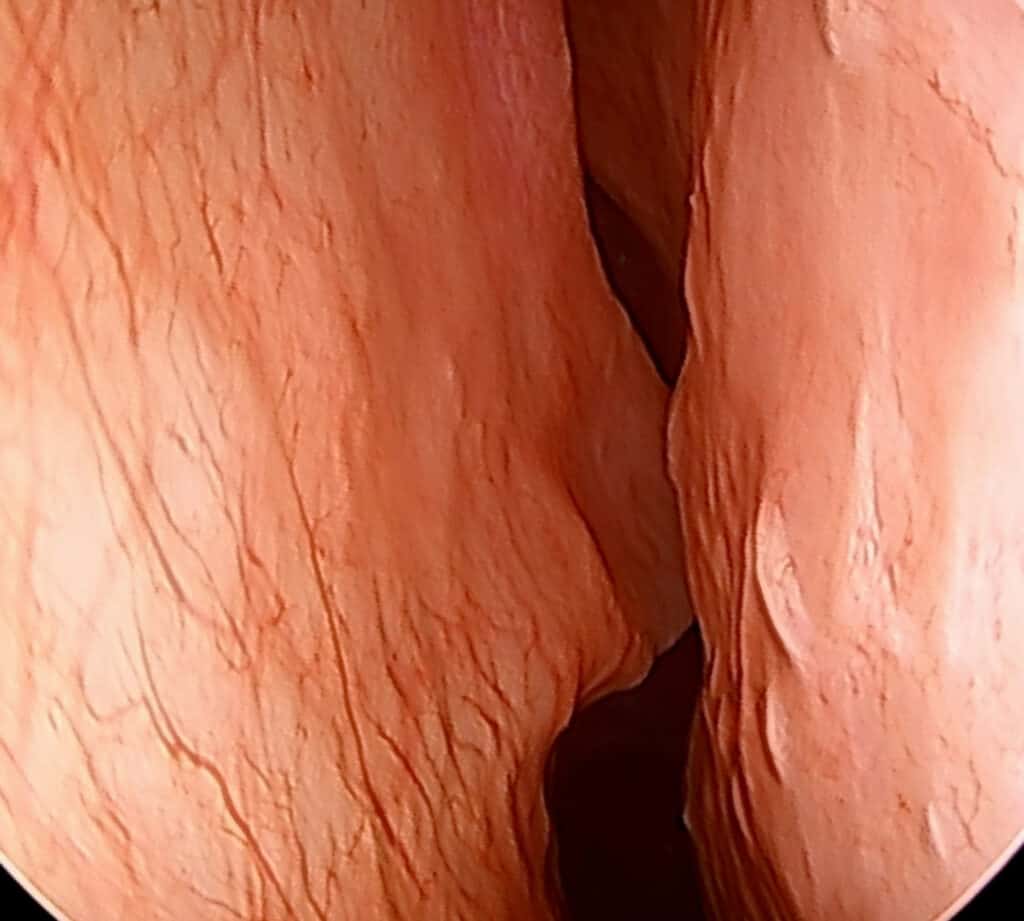
Who is a Good Candidate for a septoplasty?
Anyone with persistent nasal congestion due to a deviated septum that is not responsive to medical therapy is a great candidate for a septoplasty.

How is a Septoplasty Performed?
Septoplasty can be done under general anesthesia or in the office under IV sedation.
The deviated portions of septal cartilage and bone are accessed through an incision inside the nostril. We then trim, straighten, or reposition the septum into the proper midline position.
Splints that stay in place for 5 days may be needed to stabilize the septum as it heals.
What is Recovery Like After Septoplasty?
Patients may have nasal congestion, pain, and headaches for a few days after surgery. Most people can return to normal non-strenuous activities in 3-5 days. No heavy lifting should be done for 2 weeks. Complete healing takes around 6-8 weeks.
What are the Benefits of Septoplasty?
- Improved nasal breathing
- Facial pain and sinus pressure usually improve
- There is usually a decrease in the number of sinus infections
Our Team

James Atkins, MD
Dr. Atkins is a sinus expert with years of experience in providing compassionate and effective care to patients. He takes a personalized approach to treatment and is dedicated to helping you feel your best.

James M. Ferris, PA-C
Mike and Dr. Atkins have been practicing together for 18 years. He has a great personality and is a superb provider. Mike is personable and an invaluable asset to our practice. Just don’t start talking about fishing. You won’t be able to get him to stop.
What Patients Are Saying About Us
Our Latest Blogs

Do your ears bother you when flying
These tips may help your ears and sinuses feel better when you fly.

Dust Off Dust Mites: 10 Proven Strategies
Dust mites can be pesky. These 10 tips can help you keep your house clean.

Is Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy the Cause of Your Nasal Congestion?
Does your congestion alternate from side to side? Enlarged turbinates may be the answer.

